线性回归的几种简单解法总结
最小二乘 和 正规方程
假设线性回归方程为 $Y = W_0+W_1X1+W_2X_2+….$
则最小二乘的条件是 $S =\sum_1^n(y_i-(w_0+w_1x_{1i}+…))^2 = min$ 且
$$\frac{\sigma S}{\sigma x_i} = 0$$
令$X=\begin{bmatrix}
1&x_1^1&\cdots&x_n^1\
1&x_1^2&\cdots&x_n^2\
\vdots&\vdots&\ddots&\vdots\
1&x_1^n&\cdots&x_n^n\
\end{bmatrix}$
$Y =\begin{bmatrix}
y_1\
y_2\
\vdots\
y_n
\end{bmatrix}$
$W=[W_0,W_1,W_2,W_3 ,….]$
则 $Y=XW^T$
$\sum_1^n(y_i-(w_0+w_1x_{1i}+…))^2$
$=(XW^T-Y)^T(XW^T-Y)$
$=(WX^T-Y^T)(XW^T-Y)$
$=WX^TXW^T-Y^TXW^T-WX^TY+Y^TY$
对W求导,可得
$2WX^TX-2Y^TX=0$
$W=(Y^TX)(X^TX)^{-1}$
$W^T=(XX^T)^{-1}X^TY$
1 | # 1 正规方程解法 |
梯度下降
假设函数 $h(X)=w_0+w_1x_1+ …$
代价函数 $J(W)=\frac{1}{2n}\sum_1^n(h(x^i)-y_i)^2$
梯度下降算法 $w_i=w_i-\alpha \frac{J(W)}{\alpha w_i}$ 其中$\alpha$为学习率
即为 $w_i = w_i - \alpha \frac{1}{n}(h(x^i)-y_i)x_i$
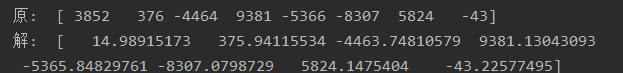
样例如下:
1 | import numpy as np |